1. View the connected disks#
sudo fdisk -l
Find the mounted disk
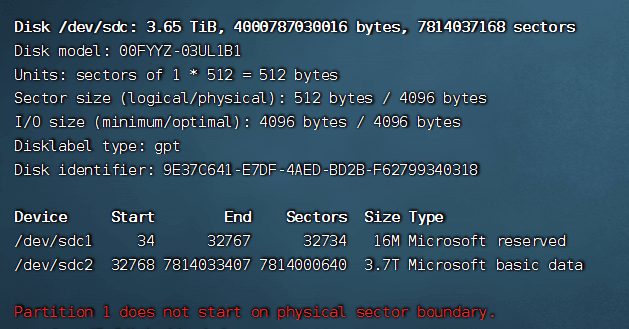
2. Partition#
sudo fdisk /dev/sdc
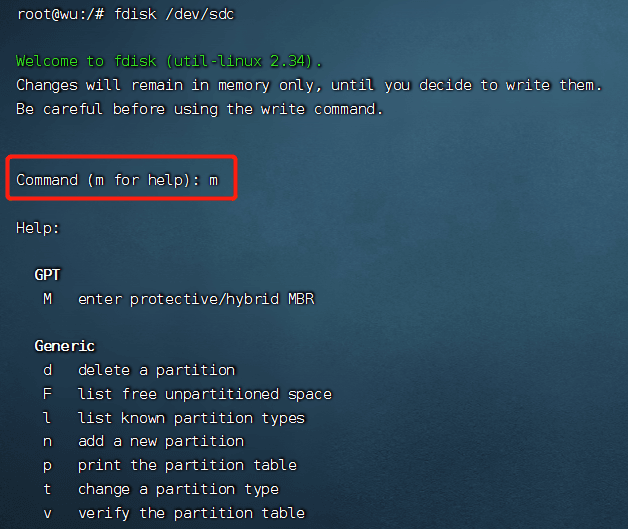
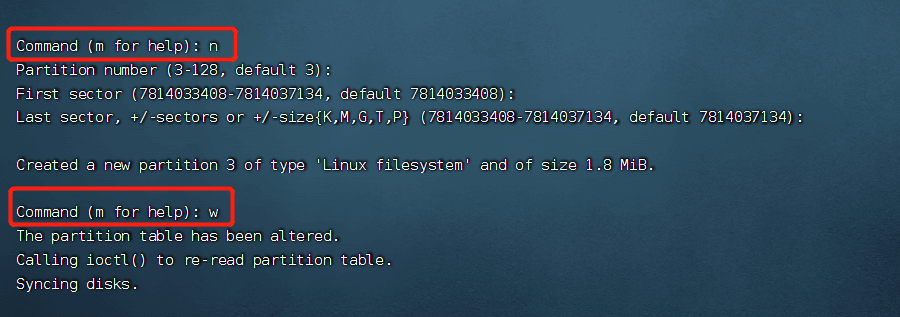
Check if the partition is created
sudo fdisk -l
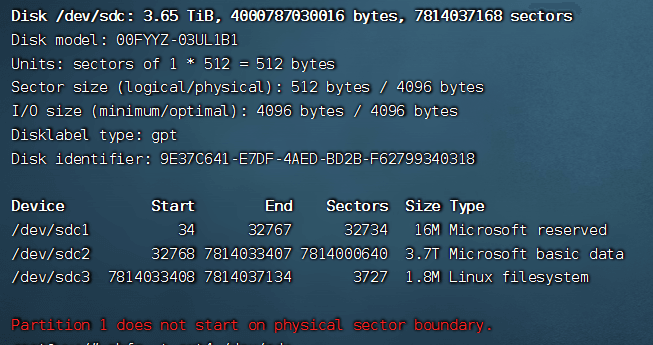
3. Format the disk as ext4#
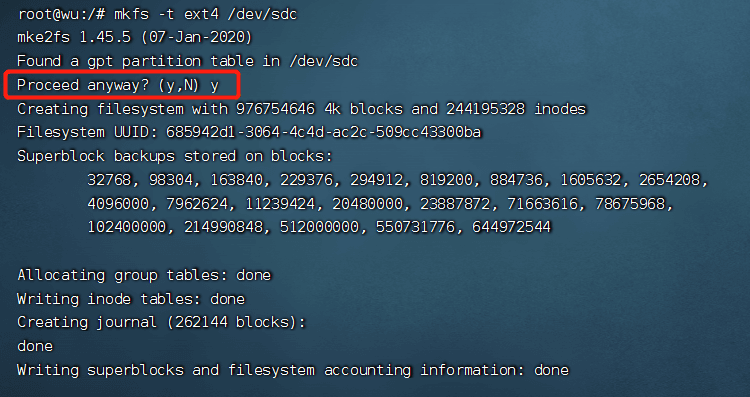
Check the disk partition
sudo lsblk
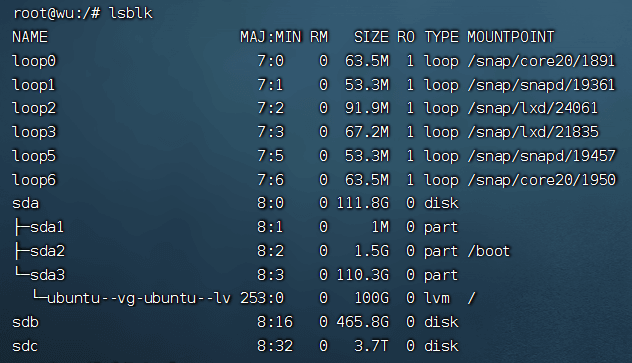
4. Mount#
Create a new directory and mount the new partition
1) Create a new temporary directory#
sudo mkdir /mnt/newpart
2) Mount the new partition to the directory#
sudo mount /dev/sdc /mnt/newpart
3) If you want to mount it under the /home directory#
Go to the home directory and move the files to the temporary directory
cd /home
sudo cp -ax * /mnt/newpart
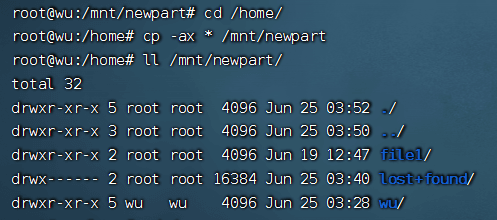
4) Rename the original home directory and create a new home directory#
mv /home /home.old
mkdir /home

5) Remount the disk to the home directory#
Mount to the home directory
sudo mount /dev/sdc /home
Check the disk mounting status
df /home
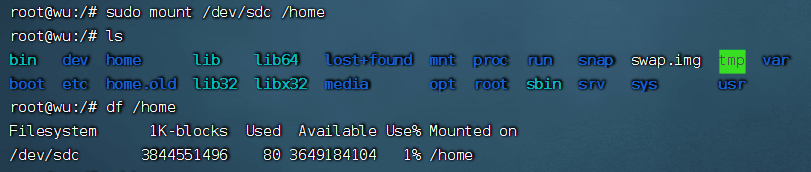
6) Set automatic mounting on startup#
Modify /etc/fstab
vi /etc/fstab
If not modified, it will still need to be remounted on the next startup.
Two methods to add mount partitions, the second method is recommended
Method 1: Use the device name directly#
/dev/sdc /home ext4 defaults 0 0
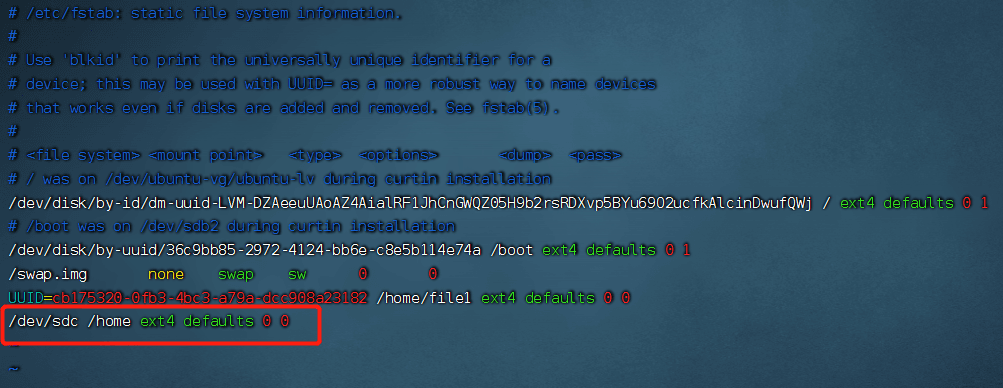
Method 2: Use the UUID of the disk#
Check the UUID of the disk
blkid
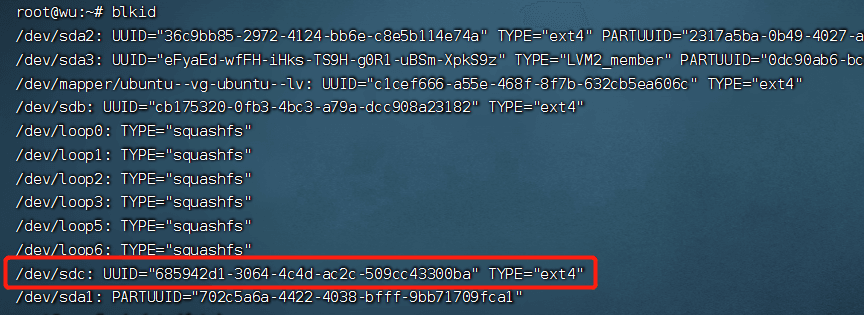
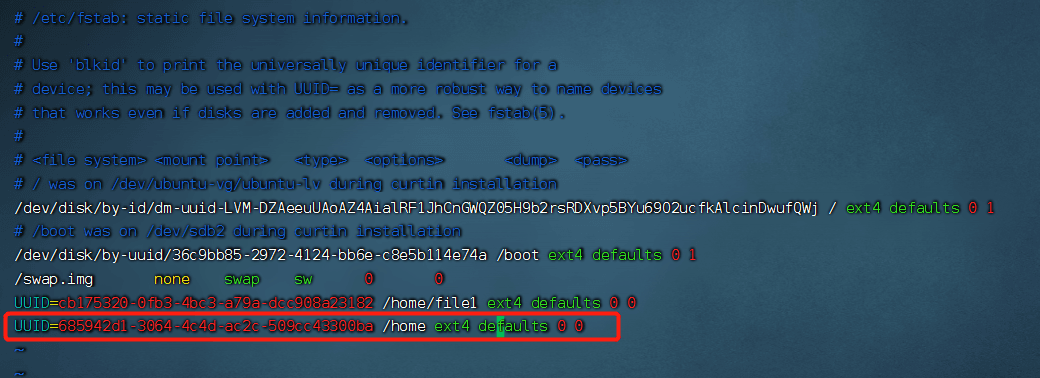
Mount using the UUID
Difference between the two methods:
If using the device name (/dev/sdc) to mount the partition, it is fixed. If the slot order of the disk changes, there may be a mismatch in the name because the name can change.
If using the UUID, each partition will have a UUID as a unique identifier after formatting. Using the UUID to mount will not cause any confusion.
Note:
In UUID=685942d1-3064-4c4d-ac2c-509cc43300ba /home ext4 defaults 0 0,
The fourth column defaults refers to the file system parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Defaults | Set of default parameters including rw, suid, dev, exec, auto, nouser, async, etc. |
| Async/sync | Set whether to run in synchronous mode, default is async |
| auto/noauto | Whether the file system is actively mounted when the mount -a command is executed. Default is auto |
| rw/ro | Whether to mount in read-write or read-only mode |
| exec/noexec | Limit whether "execute" operations are allowed within this file system |
| user/nouser | Whether users are allowed to mount using the mount command |
| suid/nosuid | Whether SUID is allowed |
| Usrquota | Enable disk quota mode for the file system |
| Grpquota | Enable group disk quota mode for the file system |
The fifth column 0 refers to whether it can be affected by the dump backup command.
Dump is a command used for backup. Usually, the value of this parameter is 0 or 1.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Do not perform dump backup |
| 1 | Perform dump operation every day |
| 2 | Perform dump operation on an irregular basis after level 1 is completed |
The sixth column 0 refers to whether sector checking is enabled.
During the boot process, the system will check if our system is intact (clean) by default.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Do not check |
| 1 | Check at the earliest (usually selected for the root directory) |
| 2 | Check after level 1 check is completed |
Save and execute
sudo mount -a
7) Check the disk status#
df